What are Chromosomes?
Inside the nucleus, Chromosomes are the thread like structure of Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and proteins (Histones and non-histones) present in most living cells in the form of genes (unit of heredity) which contains all the genetic information. The chromosomes were first described in 1875 by Strausberger and the term chromosomes was first used in 1888 by Waldeyer. Chromo means color Soma means body. They are given this name because they have a marked affinity for the basic dyes. The number of chromosomes in the nucleus is directly proportional to the quantity of DNA inside a cell.
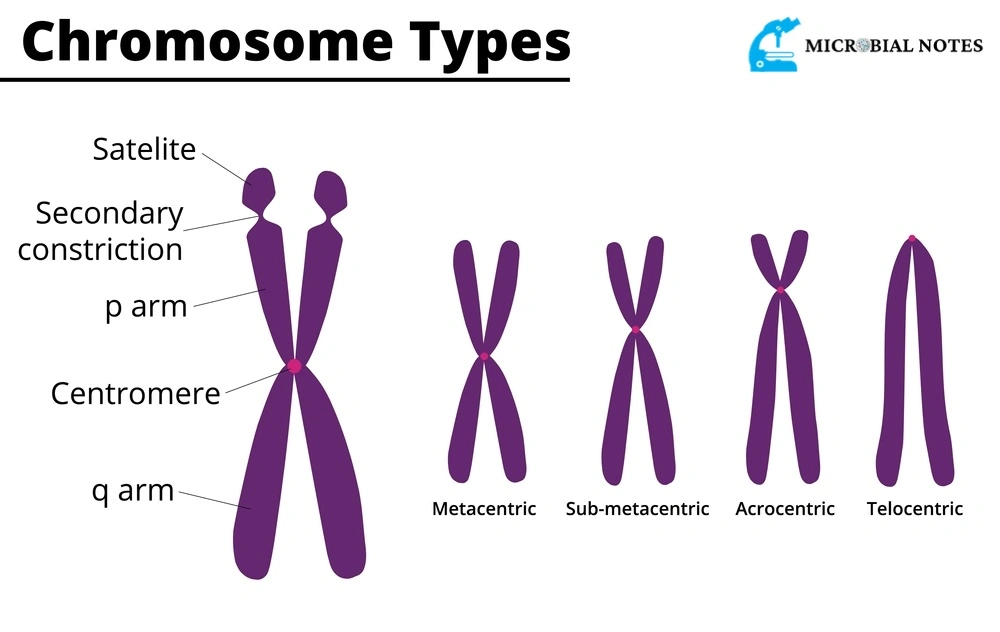
- Each chromosome is made up of two identical strands known as chromatids which are joined at the centromere with the terminal regions known as a telomere.
- Circular double stranded DNA molecule which is almost protein free is present in Prokaryotic chromosomes.
- Linear double stranded DNA molecule complicated throughout their length with proteins is present in the Eukaryotic chromosome.
Functions of chromosomes
- Chromosomes have two basic functions the first one is constant transmission and the second one is the appropriate expression of genetic information.
- During cell division, Chromosomes allow the DNA to be copied accurately.
- Gene regulation, protein synthesis, and cellular replication are also carried by the chromosomes.
Morphological structure of chromosomes
During cell division, the following structures can be seen by staining with the help of a light microscope.
Chromatid
Two identical halves of a chromosome are called chromatids. During mitosis and meiosis, chromatids are produced from the chromatin fibers. Chromatids consist of DNA and proteins and when the DNA is wrapped around these proteins it is called Nucleosomes. Chromatids help the cell to replicate and thus play role in cell division. A pair of sister chromatids is called a dyad. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids which are joined with each other with the help of cohesins.
Telomeres
At the ends of linear eukaryotic chromosomes, telomeres are specialized DNA Protein complexes. The two ends of the chromosomes are called telomeres. They cap and provide protection at the ends of the chromosomes.
Kinetochores
It is a protein structure that provides the points of attachment where spindle fibers attach to pull the sister chromatids apart during the cell division and present at the center of the chromosome called a centromere. Chromosomes can only bend at the site of primary constriction during the anaphase.
Primary constriction
The chromatids of the chromosomes are attached to each other by primary constriction. In simple words, the centromere of the chromosome is called primary constriction.
Secondary constriction
In addition to the primary constriction or centromere, the constricted region present at any point on the chromosome is called secondary constriction. It may be present in the short arm or long arm near the centromere. The main purpose of this constriction region is that it is used in the identification of chromosomes from a set. During anaphase in a cell, there can be zero, one, two, three, or four secondary restriction sites. They are also called Nucleolar organizers because they represent the sites of nucleolus formation.
Centromere
It is the region where the two sister chromatids are held together. It provides the site for the attachment of the spindle fibers during cell division.
Types of chromosomes
On the bases of the location of the centromere, a chromosome is divided into four types
Metacentric
If the centromere is present in the middle of the chromosome dividing the chromosomes in two arms of roughly equal length it is called Metacentric.
Sub metacentric
If the centromere is present near the middle of chromosomes and thus has a long arm or a short arm it is called Sub metacentric. A human’s second number chromosome is metacentric.
Acrocentric
If the centromere is located near the end of the chromosome it is called Acrocentric. Five pairs of autosomal chromosomes are acrocentric (13,14,15,21 and 22). The Y chromosome is also acrocentric.
Telocentric
If the chromosome is located at one end it is called Telocentric.
Chromosomes undergo major changes in the cell cycle
- Especially at the S-phase when they replicated and the M-phase where the separation of the replicated chromosomes occurs and set apart into two daughter cells.
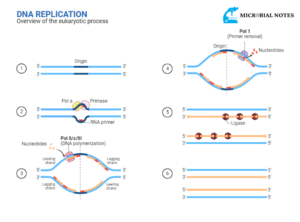
- When DNA replication occurs at the S-phase, it produces double stranded DNA molecule that is held together at the specialized location which is known as Centromere, and these are called Sister Chromatids when sister chromatids are held together at the centromere.
- The optimal time for viewing the chromosomes under the microscope is at the Metaphase stage of the M phase when the chromosomes are so highly condensed that the gene expression is uniformly shut down. When the GC-rich or AT-rich regions are stained with dyes that bind preferentially to these regions it allows the different chromosomes to be differentiated and thus give reproducible chromosome banding patterns.
- The interphase is the longest phase of the cell cycle. Before moving into the mitosis during interphase cell grows and copies its DNA before moving into mitosis then during the mitosis chromosomes will first align, separate, and at last move into the new daughter cells. During interphase that separates successive M-phases, commonly chromosomes have very long extended structures. They are not visible under optical microscopy. Here the meaning of extended structure is that the genes are efficiently expressed. During the Interphase, some regions of the chromosomes are highly condensed (Heterochromatin) these regions are transcriptionally inactive and others are extended which allows gene expression (Euchromatin).
- Sperm and egg cells are haploid means they have one copy of each chromosome, But most of the cells have two sets of chromosomes (Diploid).
- A diploid zygote is formed when a haploid egg is fertilized by the haploid sperm. From this diploid zygote, all the other cells arise by cell division.
- If an abnormal number of chromosomes occurs sometimes but if present in most of the cells of the body it will be lethal.
- When the genes are deleted and incorrectly expressed by breaks in the chromosomes it leads to structural chromosomal abnormalities.
- To transmit DNA faithfully from the mother cell to the daughter cell for the eukaryotic chromosome we required three essential and functional elements which are the following
- Centromere ( during the cell division it ensures that the segregation of the chromosomes occurs accurately)
- Replication origins ( which starts the replication)
- Telomere ( it protects the internal DNA from being degraded by nucleases by providing the cap to chromosomes)
Difference between Heterochromatin and Euchromatin
| Heterochromatin | Euchromatin |
| Highly condensed chromosomal region | Extended chromosomal region/less condensed |
| Transcriptionally Inactive | Allow the gene expression |
| Gene- poor | Gene-rich |
| Late replicative | Early replicated |
| Present only in the Eukaryotic genome | Present in both prokaryotic and Eukaryotic genome |
| Present at the Nucleus periphery | Present inside of a nucleus |
| Usually sticky in nature | Not sticky in nature |
| Darkly stained by G bands | Lighter stained with C bands |
| DNA density is high | Low density DNA |
| Makes up 97 -98% of the genome | Makes up 2-3% of the genome |
| Contains more DNA | Contains less DNA |
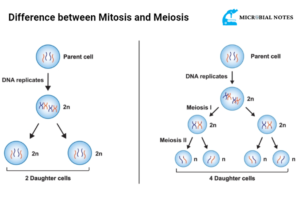
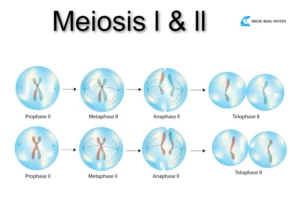
Difference between Mitosis and Meiosis
| Mitosis is the normal form of cell division | Meiosis is specialized reductive cell division |
| Daughter cells diploid | Daughter cells are haploid |
| Daughter cells are genetically identical | Daughter cells are genetically diverse |
| No tetrad formation | Tetrad formation occurs |
| Occurs in somatic cells | Occurs in Germ cells |
| Two daughter cells are formed | Four daughter cells are formed |
| The chromosome number remains the same | Chromosome numbers are reduced to half |
| In chromosomes, no Crossing over occurs | Crossing over occurs |
| Division of the nucleus occurs only once | Division of the nucleus occurs twice |
| Occurs frequently | Occurs less frequently |
| No pairing of Synapsis occurs | The pairing of Synapsis takes place |
| In all organisms, it occurs except viruses | In Plants, animals, and fungi it occurs |
| Occurs in all tissues | Occurs in specialized germ cells in the testis and ovary |
| Per cell division one round of replication | Per two cell divisions only one round of replication |
| Short approximately 30 minutes in a human cell | Can takes decades to complete |
Reference
- Hardin, J., Bertoni, G., & Becker, W. M. (2018). Becker’s world of the cell. Pearson.
- Strachan, T., & Read, A. P. (2020). Human molecular genetics. CRC Press.