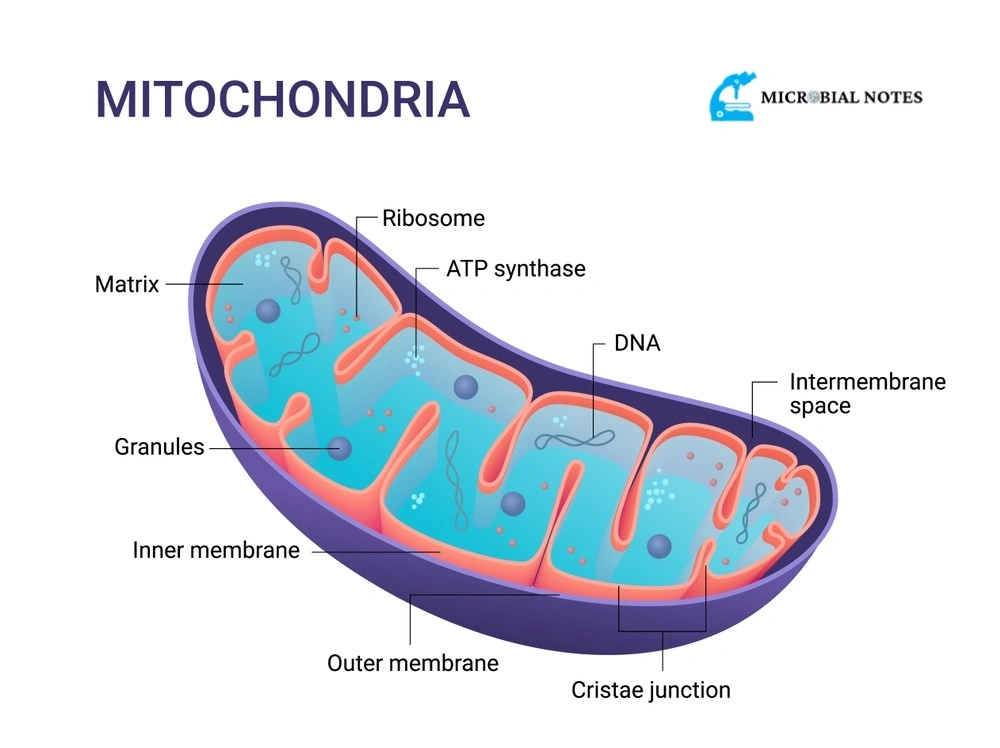
Mitochondria (singular: mitochondrion) are from the Greek language and are made up of two words ”mito” and ”chondria”. ”Mito” means ”thread” and ”chondria” means ”tiny granules”. it can be seen under the light microscope but can be seen in detail under an electron microscope.
- The singular form of mitochondria is called the mitochondrion.
- The structure is double membrane bounded.
- It is oval or rod-shaped.
- Its size is 0.5 to 1 micrometer.
- Mitochondrion is also called the powerhouse of the cell.
- They are self-replicating organelles.
- Only found in eukaryotes.
(Eukaryotes: They are the organisms that have clear nuclei e.g. fungi, bacteria, algae, protists, etc).
- It has two membranes inner and outer which are made up of proteins.
- The inner membrane has many folds called cristae. A singular form is called crista.
- A gel-like material present in it is called a matrix. But it is inside the mitochondrion so it is called the inner mitochondrial matrix.
Components of Mitochondria
Different components of mitochondria are:
- Outer Membrane
- Intermembrane space
- Lamella
- Inner membrane
- Mitochondrial DNA
- Matrix Granule
- Ribosome
- ATP synthase
Outer Membrane:
The outer membrane is smooth. In the outer membrane, a large number of proteins present are called porins.
Intermembrane Space
The space between the outer and inner membrane is called Intermembrane space. The space between the inner and outer nuclear membranes of the nuclear envelope is called perinuclear space. It plays role in the regulation of respiration and metabolic functions.
Lamella:
Any thin layer of organic tissue is termed lamella. For example, in chloroplasts, many thylakoid membranes work together which is a lamellar system.
Inner membrane:
Inner membranes have different structures inner boundary membrane, Cristal membrane, cristae, and matrix.
Mitochondrial DNA
The DNA located in the mitochondrion is called mitochondrial DNA. It is abbreviated as mtDNA or mDNA. It is a small portion of DNA in the eukaryotic cell.
Mitochondrial DNA is a circular molecule that is much smaller than nuclear DNA and is found in the matrix of the mitochondria. Mitochondrial DNA codes for a small number of proteins that are important for the function of the mitochondria, including proteins involved in energy production and the synthesis of certain lipids.
Matrix Granule
Some granules are present in mitochondria. The matrix granules create sites between the outer and inner membrane present in mitochondria in which enzymes can function expertly.
Ribosomes
Tiny granules that are freely floating in the cytoplasm. They are not membrane-bounded but are also present in prokaryotes. (Prokaryotic ribosomes are smaller than eukaryotic ribosomes). They are the sites of protein synthesis. A large number of ribosomes are found throughout the cell. if ribosomes are not working they divided themselves into two smaller units called larger subunit and smaller subunit.
ATP synthase
History:
In 1929, ATP was discovered by Karl Lohmann. It proposed the main energy transfer molecule in the cell.
ATP molecule has three subunits (a) adenine- a double ring nitrogenous base (b) a ribose – five-carbon sugar (c) 3 phosphate group in a linear chain. It stores and releases energy due to its molecular structure. The major currency of all cells is a nucleotide which is called ATP (adenosine triphosphate). The main function of mitochondrion is to synthesize ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) in the F1 sector.
The function of an inner mitochondrial matrix
Increase the surface area of the inner membrane where membrane-bounded reactions occur. Its membrane is also similar to other membranes. Mitochondria have their DNA and ribosome. The mitochondrial ribosome is more similar to bacterial ribosomes than eukaryotic ribosomes. Mitochondria are sites of aerobic (make food in the presence of oxygen) respiration. A major role is the energy production center. Mitochondria are also called the powerhouse of the cell. They are self-replicating organelles.
Under the electron microscope, it has complex morphology but under a compound microscope, they show vesicles, rods, or filaments. The presence of DNA and ribosome specify that some proteins are blended in it.
The mitochondrial matrix consists of a large number of enzymes, co-enzymes, and organic and inorganic salts that can help in different metabolic processes like aerobic respiration, the Krebs Cycle, and fatty acid metabolism. As a result of these processes the energy that is present in food is converted into an energy-rich compound called adenosine tri-phosphate ATP then allows energy to a cell on demand e.g. heart, liver, muscles, and brain that`s why called the powerhouse of cells.
Almost 90% of energy in our body cells 45% of heart muscle cells and 25% of liver muscle cells are made because of mitochondria.
Most Important and Major Roles of mitochondria
The most important and major roles of mitochondria are in the:
- Energy Production
- Redox Balance
- In Disease
Energy Production
The process of energy production is done in the inner membrane. In ATP formation redox reactions are involved in it.
Redox-Reactions are oxidation-reduction reactions. Many life processes in organisms help in a constant flow of energy. This energy is involved in processes like growth, movement, reproduction, etc. They are a direct source of energy and involvement in the changing of electrons. Due to this energy is released. How?
Aerobic Respiration produces ATP. ATP is the main energy source for different cellular functions like endocytosis, exocytosis, active transport, the transmission of nerve impulses, movement, and synthesis of macromolecules e.g. DNA, RNA, and proteins. The ability of ATP to store and release energy is because of its molecular structure. When ATP breaks down ADP (adenosine-di-phosphate) and the phosphate group is formed and energy is released. When ADP breaks down a phosphate group and AMP (adenosine monophosphate) is formed but AMP happens only in some cases. Mostly ADP recombines with the phosphate group to form ATP. So, we can say that ATP is an energy-consuming and energy-releasing process. From, this process, ATP transfers energy between metabolic reactions.
Redox Balance
Redox signaling has major roles e.g. in the heart, cardiomyocyte differentiation and excitation-contraction coupling are under tight redox control. Cardiac pathologies such as reperfusion injury, heart failure, and arrhythmias can be prevented or blocked by inhibiting specific processes.
Cell Signaling
Some superoxide forms in the live cells of mitochondria. MitoSOX Red is used for the measurement of superoxide formation in the mitochondria of live cells.
In Disease
Severe disorders of mitochondria have a great impact on human health. It affects the brain and heart and also affects various organs. Common diseases include impaired physical or cognitive development, deafness, blindness, myopathy, strokes, and other mitochondrial stresses. Severe mitochondrial diseases can cause death, especially in children.